Daily Archive: Dezembro 26, 2022
Isometrias: Matematicamente Falando 8 - Pág. 93 Ex. 4
Enunciado
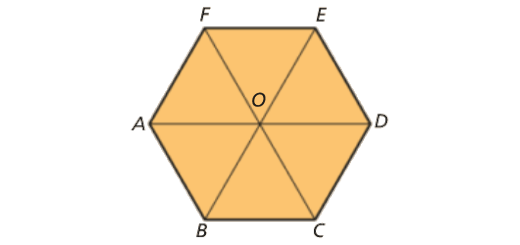
A figura representa um hexágono regular dividido em seis triângulos geometricamente iguais.
Usando letras da figura, determina:
- \(\overrightarrow {BC} + \overrightarrow {BO} \)
- \(\overrightarrow {OD} + \overrightarrow {BC} \)
- \(\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {CF} \)
- \(\overrightarrow {DE} + \overrightarrow {FO} \)
- \(B + \overrightarrow {OE} \)
- \({T_{\overrightarrow {EF} }}\left( O \right)\)
- \(\left( {{T_{\overrightarrow {AF} }} \circ {T_{\overrightarrow {FO} }}} \right)\left( A \right)\)
- \(E + \overrightarrow {AB} \)
Resolução >>
Resolução
<< Enunciado…
Ler mais
Isometrias: Matematicamente Falando 8 - Pág. 93 Ex. 3
Enunciado
Determina \(\vec a + \vec b\) em cada caso.
Resolução >>
Resolução
<< Enunciado…
Ler mais
Isometrias: Matematicamente Falando 8 - Pág. 93 Ex. 2
Enunciado
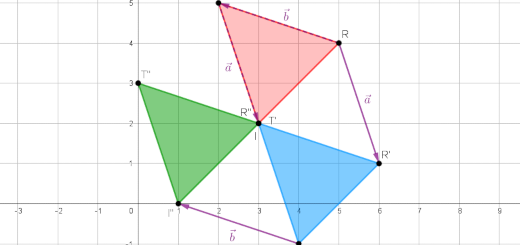
Considera o triângulo [TRI] cujas coordenadas são \(T\left( {2,5} \right)\), \(R\left( {5,4} \right)\), \(I\left( {3,2} \right)\) e os vetores \(\vec a = \overrightarrow {TI} \) e \(\vec b = \overrightarrow {RT} \).
- Desenha o triângulo [TRI] num sistema de eixos cartesianos.
- Aplica ao triângulo [TRI] a translação de vetor \(\vec a = \overrightarrow {TI} \).
Designa o novo triângulo por [T’R’I’].
- Aplica ao triângulo [T’R’I’ a translação de vetor \(\vec b = \overrightarrow {RT} \).
Designa o
…
Ler mais
Isometrias: Matematicamente Falando 8 - Pág. 93 Ex. 1
Enunciado
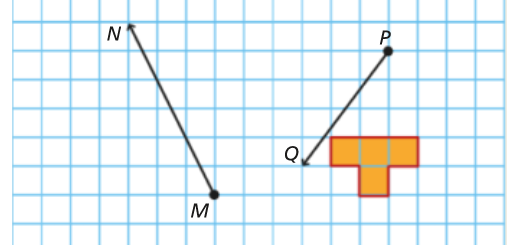
Copia a figura para o teu caderno.
Constrói a imagem do octógono pela translação de vetor \(\overrightarrow {MN} \), seguida da translação de vetor \(\overrightarrow {PQ} \).
Resolução >>
Resolução
<< Enunciado…
Ler mais
Isometrias: Matematicamente Falando 8 - Pág. 89 Tarefa 7
Enunciado
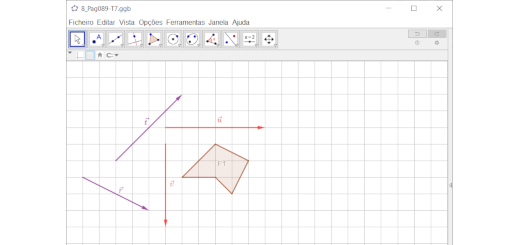
Observa a figura.
- Usando as quadrículas do teu caderno ou um programa de geometria dinâmica, como, por exemplo, o GeoGebra, reproduz a figura F1.
- Desenha a figura F2, imagem da figura F1, pela translação de vetor \({\vec u}\).
- Representa a figura F3, imagem da figura F2, pela translação de vetor \({\vec v}\).
- Há uma translação que transforma diretamente a figura F1 na figura F3.
Representa o vetor \({\vec w}\) dessa translação.
- Determina a figura F4, imagem
…
Ler mais